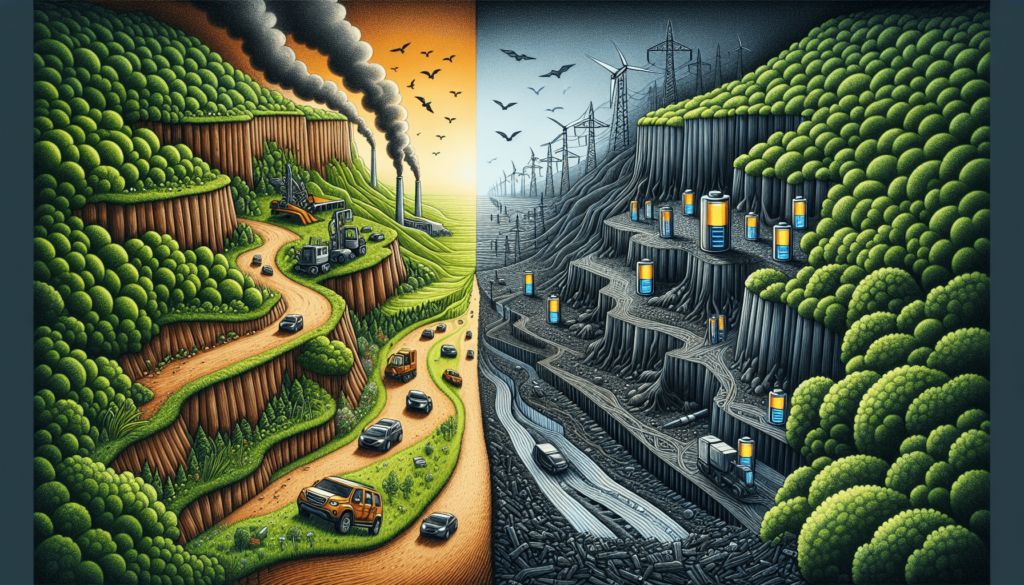
Picture a world where electric cars whisk by silently, and every home is powered by renewable energy stored in sleek, efficient lithium batteries. Sounds like a clean energy utopia, right? But before you trade in your gas guzzler and invest in solar panels, you might be wondering about the darker side of this green revolution. It’s crucial to compare the environmental footprint of lithium batteries to the one left behind by fossil fuels. Are lithium batteries actually worse for our planet, or could they be the key to a sustainable future? Let’s peel back the layers and explore the impacts of transitioning from fossil fuels to lithium-based solutions for our energy needs.
Overview of Energy Sources
Getting acquainted with the energy sources that power our world is like peeking under the hood of our global, ever-moving engine. You might be hearing a lot about lithium batteries and fossil fuels, so let’s dive into what they actually are and the role they play today.
Definition of lithium batteries
When you think about lithium batteries, picture this: small, lightweight powerhouses that energize everything from your smartphone to electric vehicles (EVs). At their core, these are rechargeable batteries where lithium ions move from the negative electrode to the positive electrode during discharge and back when charging. They’re kind of the celebrities of the energy storage world right now, thanks to their efficiency and portability.
Explanation of fossil fuels
On the other end of the spectrum, fossil fuels are like the old giants of the energy scene. They’ve been around for millions of years, formed from the buried remains of plants and animals subjected to intense heat and pressure. Coal, oil, and natural gas make up this group, and they have been powering industries, vehicles, and electricity generation for ages.
Current global energy landscape
Imagine a giant, bustling marketplace, but instead of fruits and veggies, it’s all about energy. Fossil fuels have been leading the charge for centuries, but there’s a new vendor in town: lithium batteries, alongside other renewables, are making waves. This shift is due in part to a growing awareness of climate change and the need for cleaner, more sustainable energy solutions.
Environmental Impact
When we talk about the environment, it’s all about the footprint we leave behind, whether it’s carbon footprints or the impact on the land and air around us.
Carbon footprint comparison
Fossil fuels are like the heavyweight champions of carbon emissions, contributing significantly to greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. Lithium batteries, however, are more like the lightweight contenders, usually associated with lower emissions, especially when charged with renewable energy.
Pollution and toxic waste
While fossil fuels are notorious for air pollution and oil spills, lithium batteries aren’t saints, either. The extraction of lithium and the production of these batteries can lead to toxic waste challenges. It’s like choosing between two types of pollution, with each having its drawbacks.
Habitat destruction and resource extraction
Drilling for oil and mining coal can rip into natural habitats, leaving scars on the environment. Lithium mining, too, is not without its impacts, as it can deplete water sources and disturb ecosystems. It’s a reminder that no energy source is completely free of environmental baggage.
Lifecycle analysis from production to disposal
If we think of each energy source as having a life story, from birth (production) to death (disposal), it’s clear that both fossil fuels and lithium batteries have their dark chapters. The entire lifecycle of fossil fuels is fraught with environmental hazards, while lithium batteries pose challenges in recycling and the disposal of toxic components.
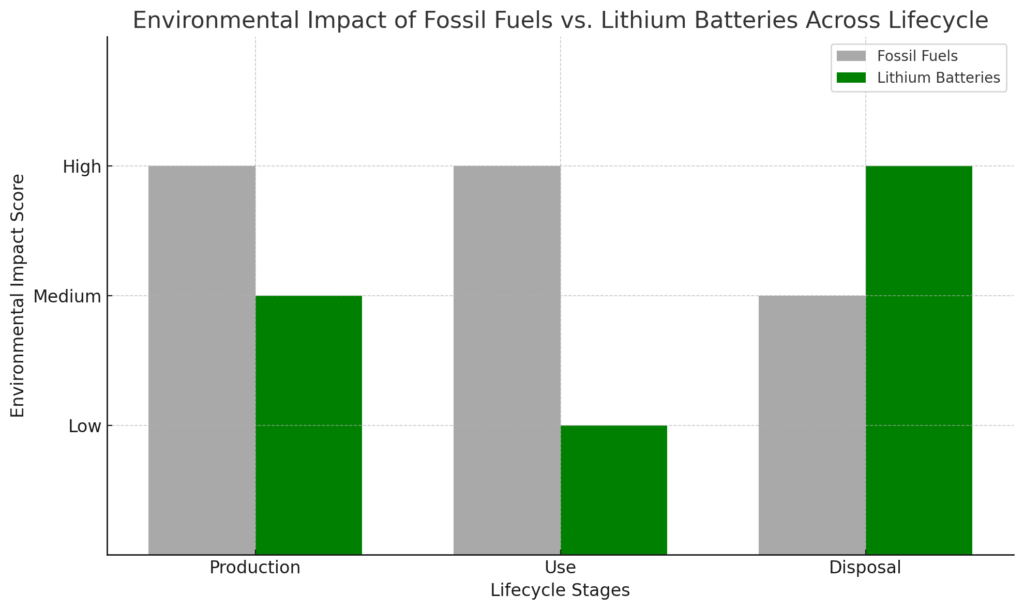
The chart above illustrates the comparative environmental impact of fossil fuels versus lithium batteries across their lifecycle stages, including production, use, and disposal. As depicted, fossil fuels have a consistently high environmental impact in production and use, with a slightly lower but still significant impact at disposal. In contrast, lithium batteries have a medium impact during production, a low impact during use, and a high impact at disposal, highlighting the challenges associated with recycling and disposing of toxic components. This visual analysis underscores the importance of addressing environmental concerns at every stage of energy production and use to achieve a more sustainable energy future.
Efficiency and Energy Storage
When it comes to doing their job – that is, powering our lives – these two players have quite different efficiency statistics and storage capabilities.
Energy density of lithium batteries vs fossil fuels
Fossil fuels have a high energy density, meaning a small amount can produce a large amount of energy. Lithium batteries, while impressive for their size, still can’t hold as much energy as an equivalent volume of fossil fuel. Yet, they’re catching up fast, and innovations continue to improve their capacity.
Charge cycles and longevity
Lithium batteries have a finite number of charge cycles before their performance starts to wane. Think of it like a battery’s lifespan, with each charge being one tick of the clock. However, they still offer a significant advantage in terms of longevity and efficiency over the use of fossil fuels, especially in applications like electric vehicles.
Efficiency in energy conversion
Here’s something lithium batteries excel in: turning energy into power with minimal loss. Fossil fuel energy conversion, like in internal combustion engines, can be quite inefficient, losing a lot of potential energy as heat. Electric motors powered by lithium batteries, however, can boast efficiency rates of over 90%.
Economic Factors
The battle between lithium batteries and fossil fuels isn’t just about energy—it’s also about money. Let’s peek into the economic arena.
Cost of production and raw materials
Extracting and refining oil or mining coal can be costly, not to mention environmentally damaging. Lithium batteries, on the other hand, require rare minerals and complex manufacturing processes, which can also be expensive. However, as technology advances, the cost of producing lithium batteries is gradually decreasing.
Market availability and demand
The demand for fossil fuels has been robust for decades, but it’s beginning to dip as renewable energy sources and electric vehicles gain popularity. Lithium batteries are in high demand, powering not only EVs but also storing energy from renewable sources like solar and wind.
Investment and future projections
Investors are increasingly turning their backs on fossil fuels and looking towards renewables and electric vehicles. This shift indicates a belief in the growth potential of lithium battery technology and its central role in a cleaner, more sustainable energy future.

Health and Safety
When we bring health and safety into the conversation, it’s evident that both energy sources come with their share of risks, but in different arenas.
Exposure to hazardous materials
The production and disposal of lithium batteries involve handling toxic materials, posing risks to workers. Similarly, the extraction and burning of fossil fuels release harmful substances into the air, affecting the health of millions.
Risk of accidents and explosions
Fossil fuels carry the risk of devastating oil spills and gas leaks. Lithium batteries, while generally safe, have had instances of overheating and catching fire, though these risks are being mitigated with advancements in technology.
Long-term health effects of pollution
The burning of fossil fuels has a profound impact on air quality, leading to respiratory and cardiovascular diseases. While the direct health impacts of lithium batteries are more localized to their production and disposal, the broader use of these batteries contributes to cleaner air and better overall health outcomes.
Renewability and Sustainability
As we gear towards a more sustainable future, it’s essential to examine the renewability aspect of our energy choices.
Renewable energy integration
Lithium batteries play a critical role in the transition to renewable energy by storing excess solar and wind power for use when the sun isn’t shining or the wind isn’t blowing. This compatibility makes them key players in a sustainable energy framework.
Recyclability of lithium batteries
While recycling lithium batteries remains a challenge, progress is being made in developing more effective and efficient recycling methods. This is crucial for minimizing the environmental impact and making the use of lithium batteries more sustainable.
Dependency on non-renewable resources
Fossil fuels are, by their very nature, finite. We’re burning through them at an unsustainable rate, and their renewability is effectively nil. In contrast, lithium batteries, especially when paired with renewable energy sources, offer a pathway to reducing our dependency on non-renewable resources.

Technological Advancements
The pace of innovation could dramatically change the landscape for both lithium batteries and fossil fuels.
Innovations in lithium battery technology
From improving energy density and reducing charging times to enhancing safety and extending lifecycles, advancements in lithium battery technology are rapidly evolving. These innovations promise to make them even more integral to our energy future.
Alternative energy storage solutions
Beyond lithium batteries, research is ongoing into alternative energy storage solutions, like solid-state batteries, hydrogen fuel cells, and ultracapacitors. These technologies might one day play significant roles in our energy ecosystem.
Fossil fuel technology advancements
Fossil fuel industries are also innovating, seeking ways to reduce emissions through carbon capture and sequestration and improve the efficiency of extraction and burning processes. Whether these efforts can sufficiently mitigate the environmental impacts, however, remains a pressing question.
Policy and Regulation
Government policies and regulations can dramatically accelerate or impede the adoption of different energy sources.
Government support and subsidies
Subsidies and incentives for renewable energy and electric vehicles are driving the adoption of lithium batteries. Conversely, subsidies for fossil fuel industries are increasingly scrutinized for their environmental impact, with calls for a shift towards supporting cleaner alternatives.
Environmental regulations
Stricter environmental regulations worldwide are putting pressure on fossil fuel industries to clean up their act, while also making the economic case for lithium batteries and renewable energy sources stronger.
International agreements and impact
Global agreements, like the Paris Agreement, aim to reduce carbon emissions and combat climate change. These agreements have a profound impact on energy policies, often favoring the development and adoption of cleaner energy technologies, including lithium batteries.

Societal Impact and Public Opinion
How society views and accepts these energy sources can influence their adoption and development.
Public awareness and education
As public awareness of climate change and environmental issues grows, so does the interest in and demand for clean energy technologies. Education plays a key role in highlighting the benefits of lithium batteries and renewable energy over fossil fuels.
Impact on local communities and indigenous lands
The extraction of both lithium and fossil fuels can have significant impacts on local communities and indigenous lands. Ensuring responsible sourcing and respecting the rights and lands of indigenous peoples are critical considerations in the energy transition.
Consumer behavior and adoption rates
The adoption rates of electric vehicles and renewable energy systems signify a shift in consumer behavior towards more sustainable energy choices. As consumers become more environmentally conscious, their choices can drive significant change in the global energy landscape.
Conclusion
When weighing the question, “Are lithium batteries worse than fossil fuels?”, it’s clear that both have their environmental and societal implications. However, in the context of climate change and sustainability, lithium batteries—paired with renewable energy—offer a path towards a cleaner, more sustainable future. They are not without their challenges, including the need for technological innovations, improvements in recycling, and ensuring ethical resource extraction. The transition away from fossil fuels requires a multifaceted approach, involving advancements in technology, shifts in policy and regulation, and changes in consumer behavior. The future outlook on energy sources suggests a gradual but significant shift towards more sustainable and renewable energy solutions, underpinned by the development and adoption of lithium batteries. As we move forward, it’s crucial to continue assessing and mitigating the environmental and societal impacts of our energy choices to foster a healthier planet for future generations.

