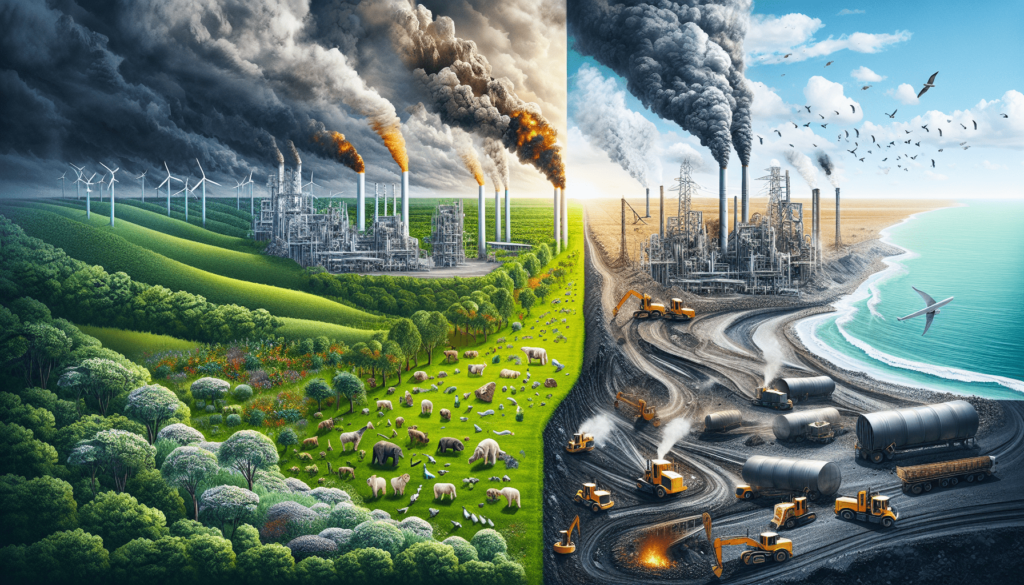
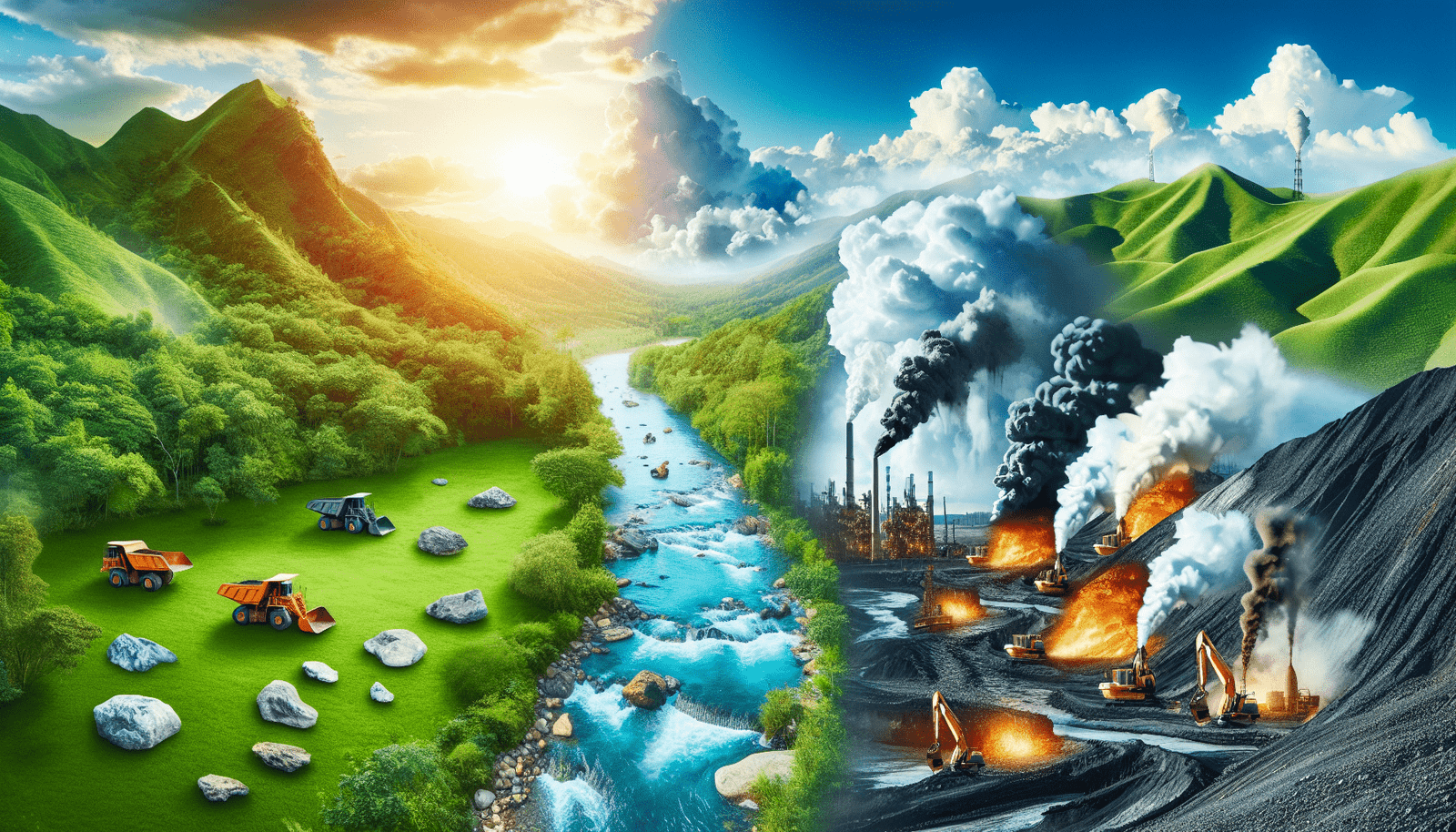
Imagine for a moment that you’re weighing the options for a cleaner future, tossing up between lithium batteries and traditional fossil fuels. It’s a hot topic right now, with everyone looking for the best route to take when it comes to powering our lives without costing the Earth. You’ve probably heard a lot about the benefits of lithium, hailed as the green energy savior; but you might also have caught whispers about its potential downsides. In “Is Lithium More Harmful Than Fossil Fuels?”, you’re about to get a clearer picture of this debate. Let’s unwrap together the complexities behind lithium mining and use, juxtaposing them with the well-documented effects of fossil fuels, to give you a better understanding of where the real harm lies.
Overview of Lithium and Fossil Fuels
Definition of lithium and its uses in modern technology
Lithium might sound like something straight out of a science fiction novel to you, but it’s actually a metal that’s become a cornerstone of modern technology. You’ll find lithium in batteries powering everything from your smartphone to electric vehicles (EVs). It’s lightweight, rechargeable, and can store a lot of energy, making it perfect for gadgets and transportation in an increasingly mobile world.
Understanding fossil fuels and their impact on the environment
On the flip side, fossil fuels — which include coal, oil, and natural gas — have been the go-to energy source since the Industrial Revolution. You use them directly or indirectly almost every day, from heating homes to fueling cars and generating electricity. However, they come with a significant environmental cost, primarily due to air and water pollution and their hefty contribution to climate change.
Comparison between lithium and fossil fuels in terms of energy production and usage
Now, when you compare lithium and fossil fuels, you’re essentially looking at two very different energy worlds. Lithium powers clean, renewable energy tech, whereas fossil fuels are all about combustion and carbon emissions. Lithium is a key player in reducing our carbon footprint, but as you’ll see, it’s not without its own issues.
Environmental Impact of Lithium Extraction
The process of lithium mining and its ecological footprint
You might be surprised to learn that extracting lithium can be quite damaging to the environment. The two main methods, mining rock and extracting from brine pools, both require significant amounts of water and land, impacting local ecosystems and wildlife. Picture massive ponds that evaporate water to leave behind lithium salts — these can be an eyesore and disrupt local habitats.
Water usage and contamination in lithium extraction
One of lithium mining’s critical issues is the sheer volume of water it consumes, which can exacerbate drought conditions in already arid areas. Moreover, the chemical processing of lithium can lead to water contamination, affecting both surface and groundwater. Local communities often bear the brunt of these impacts, facing water shortages and pollution.
Impact on local ecosystems and biodiversity
Lithium extraction doesn’t just drink up water; it also disrupts local ecosystems. The transformation of landscapes to make way for mines and evaporation ponds can lead to habitat loss for plants and animals, throwing biodiversity out of balance. It’s a challenging scenario, especially in biodiverse-rich but lithium-abundant areas.

Environmental Impact of Fossil Fuels
Air pollution caused by burning fossil fuels
You’re probably familiar with the smoggy backdrop of big cities and the part fossil fuels play in that picture. Burning fossil fuels releases a cocktail of pollutants into the air, including particulate matter, nitrogen oxides, and sulfur dioxide, which can lead to respiratory problems and other health issues in humans, not to mention the broader environmental consequences.
Water contamination from oil spills and coal mining
Fossil fuels’ relationship with water isn’t much better. Oil spills, both at sea and on land, have devastating effects on marine and terrestrial ecosystems. Coal mining, too, contaminates water bodies with heavy metals and toxins, making water unsafe for consumption and damaging aquatic life.
Greenhouse gas emissions and contribution to climate change
The elephant in the room with fossil fuels is, of course, their contribution to climate change. Carbon dioxide, a byproduct of burning fossil fuels, is the primary culprit in global warming, leading to extreme weather, rising sea levels, and other catastrophic environmental effects. It’s a global problem that requires a swift and comprehensive response.
Human Rights and Social Implications
Working conditions in lithium mines vs. fossil fuel extraction
The mining and extraction of both lithium and fossil fuels raise significant human rights concerns. Workers often face hazardous conditions, from exposure to toxic chemicals in lithium extraction to the risk of accidents and respiratory diseases in coal mines and oil fields. The quest for these resources can sometimes lead to exploitation and unsafe working environments.
Displacement of local communities and indigenous peoples
The expansion of mines and drilling operations for both lithium and fossil fuels frequently involves displacing local communities and indigenous peoples. These groups can lose their homes, land, and access to natural resources, such as clean water, with little to no compensation or consideration, sparking legal conflicts and human rights debates.
Economic benefits vs. social costs in producing regions
There’s an undeniable economic upside to mining and drilling in resource-rich areas, including job creation and investment. However, the social costs — including pollution, health risks, and cultural disruption — often outweigh these benefits for local populations. The challenge lies in finding a balance that respects both the environment and the rights of communities.
Economical Aspects
The cost-effectiveness of lithium vs. fossil fuels
When you crunch the numbers, lithium emerges as a compelling alternative to fossil fuels, primarily due to the falling costs of lithium-ion batteries and the efficiency gains in renewable energy technologies. However, the initial investment in clean technologies can be high, despite long-term savings and environmental benefits.
Investment and market trends in lithium and fossil fuel industries
There’s a clear trend of increasing investment in lithium and renewable energy markets as awareness of climate change grows and technology costs drop. Meanwhile, the fossil fuel industry faces declining investments and growing regulatory and societal pressures to reduce carbon emissions and shift to cleaner alternatives.
Government subsidies and their influence on each sector
Government policies and subsidies play a significant role in shaping the energy landscape. Subsidies for fossil fuels have historically kept some outdated and polluting technologies artificially competitive. Conversely, incentives for renewable energy and lithium-based technologies have helped drive innovation and reduce costs, although the playing field isn’t always level.
Health Risks Associated with Lithium
Exposure to lithium during mining and production
Workers in the lithium extraction and processing industry can face health risks from exposure to chemicals and lithium dust, which can lead to respiratory issues and skin irritation. The long-term health effects of such exposure are still being studied, underscoring the need for stringent safety regulations and health monitoring.
Long-term health effects of lithium on workers and local populations
The communities living near lithium mining sites are also at risk of health issues due to water contamination and air pollution. While lithium itself isn’t highly toxic, the chemicals used in the extraction process can pose significant health hazards, from altered thyroid function to neurological damage.
Safety measures and regulation in the lithium industry
Improving safety measures and regulatory oversight is crucial in mitigating the health risks associated with lithium. This includes stricter environmental controls, better protective gear for workers, and more transparent reporting of chemical usage and waste management practices. Such steps are essential for ensuring the lithium industry’s sustainable and ethical growth.
Health Risks Associated with Fossil Fuels
Health impacts of air and water pollution from fossil fuels
The health impacts of fossil fuels are well-documented and widespread. Air pollution from burning fossil fuels is linked to heart disease, stroke, respiratory diseases, and certain types of cancer. Water pollution from spills and runoff can contaminate drinking water, leading to a host of health issues, including gastrointestinal illnesses.
Occupational hazards in the fossil fuel extraction and refinery process
Workers in the fossil fuel industry face numerous occupational hazards, from the risk of explosions and fires in oil rigs and refineries to black lung disease from coal mining. The industry’s toll on workers’ health is a significant concern, often leading to lifelong health issues or premature death.
Public health initiatives to mitigate risks
Public health initiatives targeting the risks associated with fossil fuels focus on reducing emissions, improving workplace safety, and transitioning to cleaner energy sources. These include regulations on air and water quality, investment in public transportation and renewable energy, and health monitoring and support for workers in the industry.
Innovation and Technological Advances
Advances in lithium extraction and processing technology
Innovation in the lithium sector aims to make extraction and processing more efficient and less harmful to the environment. New methods, such as direct lithium extraction (DLE) from geothermal brine, promise to reduce water usage and the ecological footprint of lithium mining. Continuous improvement in battery technology also increases energy density and reduces costs.
Development of cleaner and more efficient fossil fuel technologies
Within the fossil fuel industry, technological advances focus on reducing emissions and improving efficiency. These include carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies, more efficient combustion techniques, and the development of synthetic fuels. While these technologies can mitigate some impacts, the shift towards renewable energy is crucial for long-term sustainability.
The role of innovation in reducing environmental and health impacts
Innovation plays a key role in addressing both environmental and health impacts of lithium and fossil fuels. Cleaner extraction methods, improved worker safety, and the development of sustainable alternatives to both lithium-ion batteries and fossil fuels are all areas where technology can make a significant difference. The challenge lies in balancing economic growth with environmental preservation and social responsibility.

Sustainability and Future Outlook
Lithium’s role in renewable energy and electric vehicles
Lithium is set to play a pivotal role in the transition to renewable energy and the widespread adoption of electric vehicles. Its ability to store large amounts of energy efficiently makes it essential for mitigating climate change and reducing reliance on fossil fuels. However, ensuring sustainable and responsible lithium extraction practices is crucial.
The declining reliance on fossil fuels and the transition to cleaner energy
The global movement towards cleaner energy sources is gradually reducing reliance on fossil fuels. Renewable energy sources like wind, solar, and hydroelectric power are becoming more cost-effective and efficient, driven by technological advances and environmental regulations. This transition is critical for combating climate change and safeguarding planetary health.
Sustainability challenges and potential solutions for both lithium and fossil fuels
The sustainability challenges for lithium revolve around minimizing environmental impact and ensuring ethical practices throughout the supply chain. For fossil fuels, the challenge is phasing out their use in favor of cleaner alternatives while managing the socioeconomic implications of this transition. Solutions include investing in clean technology, strengthening environmental regulations, and supporting affected communities and workers through the transition.
Final Analysis
Comparing the overall harm of lithium versus fossil fuels
When you stack lithium up against fossil fuels, the immediate reaction might be to declare lithium the clear winner due to its essential role in green technology. However, it’s not without its downsides. Environmental and social implications of lithium extraction need addressing, but when compared to the widespread and severe impacts of fossil fuels — from climate change to public health crises — lithium’s issues seem more manageable and solvable.
Considering the balance between technological needs and environmental sustainability
Finding the balance between meeting our technological needs and ensuring environmental sustainability is no small feat. It requires a multifaceted approach, including improving extraction and processing methods, developing sustainable alternatives, and implementing policies that prioritize long-term ecological health over short-term gains.
Outline of steps needed for a more sustainable and less harmful future
To pave the way for a more sustainable and less harmful future, several steps are crucial. These include accelerating the transition to renewable energy, investing in clean technology and innovation, enforcing stricter environmental regulations, and supporting communities and workers through economic transitions. Education and public awareness are also key in driving demand for sustainable practices and products. Ultimately, it’s about making informed choices that consider the broader implications for our planet and future generations.

