Imagine a world where your electric vehicle does more than just take you from point A to point B; it also plays a crucial role in powering your home or even feeding energy back into the grid. That’s exactly what Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology is all about. This innovative system allows electric vehicles to interact with the power grid, offering the ability to store energy and supply electricity back to the grid when it’s needed most. It’s a game-changer in how we think about the relationship between our transport and energy systems, making electric vehicles active participants in our energy ecosystem. So, let’s get into the nitty-gritty of what V2G technology is and how it works.
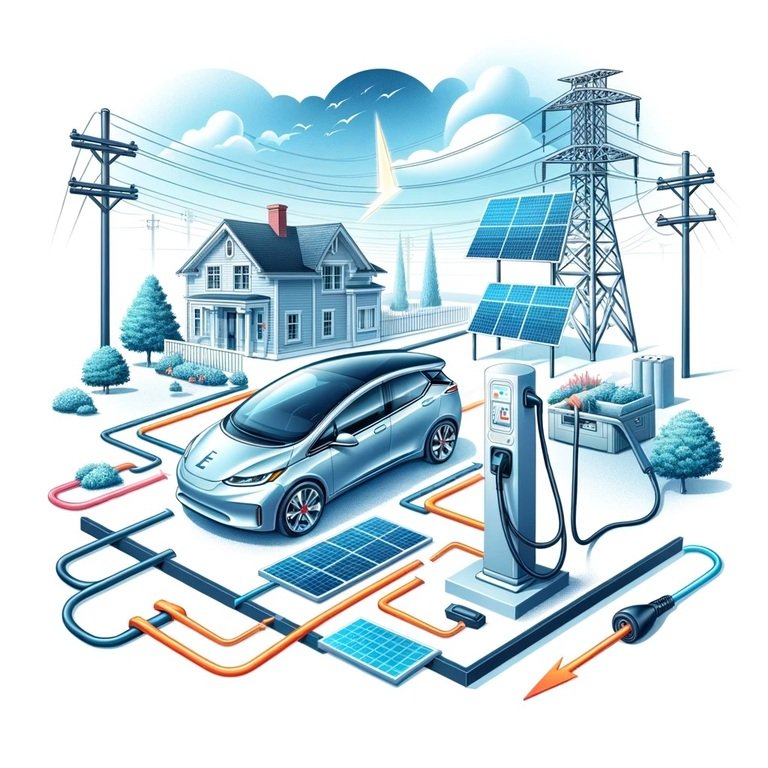

Understanding Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) Technology
Definition of V2G
Vehicle-to-Grid, or V2G, technology is a forward-thinking approach that allows electric vehicles (EVs) to communicate and interact with the power grid. Imagine your electric car not just consuming electricity but also having the ability to send it back to the grid. That’s V2G in a nutshell. It paves the way for a symbiotic relationship between your vehicle and the grid, transforming electric vehicles into mobile energy storage units.
The concept behind V2G
The core idea of V2G is pretty simple yet revolutionary. Electric vehicles have batteries that are often underutilized. What if these batteries could serve a dual purpose? Charge up when demand is low and give energy back when the grid is under stress or demand peaks. It’s like your EV helping to power the city during a scorching summer day when everybody’s cranking up their air conditioners.
Historical development of V2G technology
The journey of V2G technology began in the late 1990s and early 2000s, spearheaded by visionary engineers and researchers who saw the untapped potential of electric vehicle batteries. Over the years, advancements in battery technology, electric vehicles, and smart grid capabilities have turned the dream of V2G into a tangible reality. It’s a classic case of technology catching up to vision.
How V2G Technology Works
The role of electric vehicles in V2G
In the V2G ecosystem, electric vehicles are more than just transportation devices; they’re actively engaged in the energy market. Your EV acts as a portable power bank that can store energy and discharge it back into the grid when needed. It’s a game-changer for how we think about cars, transforming them from power consumers to power providers.
Interaction between vehicle and power grid
This is where it gets a bit more technical, but stick with me. For V2G to work, there needs to be a seamless interaction between your electric vehicle and the power grid. This involves real-time communication to manage charging and discharging activities based on grid demand, prices, and your personal preferences. It’s like your car and the grid having a constant conversation to ensure energy is used most efficiently.
Bi-directional charging system
The magic behind V2G is the bi-directional charging system. Unlike traditional chargers that only allow electricity to flow one way (into the car), bi-directional chargers enable the flow of electricity both to and from the vehicle’s battery. This means that your EV can be charged overnight using cheap, off-peak electricity, and then sell some of that electricity back to the grid during peak times at a higher price. Neat, right?
Components of V2G Systems
EVs equipped with V2G capabilities
Not all electric vehicles are created equal when it comes to V2G. For an EV to participate in V2G programs, it needs to be equipped with the right hardware and software that support bi-directional charging. This includes not just the vehicle itself but also the onboard battery management system that ensures energy is stored and released in a safe, efficient manner.
Bi-directional chargers and their functions
Bi-directional chargers are the unsung heroes of the V2G world. These devices are what make the two-way flow of electricity possible. They’re installed in homes, businesses, or public charging stations and are responsible for managing the charging and discharging processes, ensuring your vehicle’s battery is always at its optimal state, whether you’re feeding the grid or gearing up for a road trip.
Software platforms for managing V2G interactions
Finally, you can’t talk about V2G without mentioning the sophisticated software platforms that make all this possible. These platforms are the brains of the operation, coordinating between electric vehicles, charging stations, and the wider grid. They take into account energy prices, grid demand, and your personal preferences to optimize when and how your EV interacts with the grid.
Benefits of V2G Technology
Providing grid stability and reliability
One of the biggest advantages of V2G is its ability to enhance the stability and reliability of the power grid. By intelligently managing when EVs charge and discharge, V2G can help even out the peaks and troughs in electricity demand, acting as a shock absorber for the grid.
Facilitating the integration of renewable energy
V2G also plays a pivotal role in integrating more renewable energy sources, like wind and solar, into the grid. Since these sources are intermittent, V2G can help balance out their variability. EV batteries can store surplus renewable energy when production is high and then supply it back to the grid when needed.
Generating revenue for electric vehicle owners
Let’s not forget the financial incentives. For EV owners, V2G can turn your vehicle into a small business on wheels. By selling electricity back to the grid at peak times, you can earn money or credits, offsetting the cost of owning and operating an EV.

Challenges and Limitations
Technical barriers
Despite its potential, V2G faces several technical challenges. These include developing more efficient and cheaper bi-directional chargers, improving battery technology to cope with increased charge/discharge cycles, and ensuring cyber-security in the complex communication networks between EVs and the grid.
Economic and commercial challenges
There’s also the question of economics. Setting up V2G on a large scale requires significant upfront investment in infrastructure. Plus, for V2G to be attractive to consumers, the financial returns from participating need to outweigh the potential increased wear on EV batteries.
Regulatory and market hurdles
Finally, the regulatory landscape needs to catch up. V2G touches on various domains – transportation, energy, environment – each with its own set of rules and stakeholders. For V2G to flourish, coherent policies and standards that encourage its adoption are needed.
The Future of V2G Technology
Innovations in battery and charging technology
The horizon looks bright for V2G, with ongoing advancements in battery chemistry and charging infrastructure. Innovations like solid-state batteries could increase energy density and reduce charging times, making V2G more practical and efficient.
Potential impacts on the electric power grid
As V2G technology matures, it’s poised to radically transform the electric power grid, making it more resilient, flexible, and capable of supporting a higher penetration of renewable energy sources. It offers a glimpse into a future where energy is more decentralized and democratic, with individual EV owners playing a pivotal role.
Growing adoption and scalability issues
The path to widespread V2G adoption is not without its bumps. Scalability is a critical issue, with questions around how millions of EVs can be seamlessly integrated into the grid without overwhelming existing infrastructure. Nonetheless, the potential benefits make it a challenge worth tackling.

Environmental Impacts of V2G
Reduction in carbon footprints
By enabling more efficient use of renewable energy and enhancing grid stability, V2G can significantly reduce carbon footprints. It represents a meaningful step towards decarbonizing not just the transportation sector but the entire energy system.
Support for renewable energy sources
V2G technology bolsters the case for renewable energy by solving one of its biggest challenges – the intermittency of supply. With V2G, electric vehicles essentially become mobile energy storage solutions, helping to smooth out the peaks and valleys in renewable energy production.
Overall environmental benefits
The environmental impact of V2G extends beyond just carbon emissions. By promoting the use of electric vehicles and making the energy system more efficient and less reliant on fossil fuels, V2G can play a crucial role in reducing air pollution and fostering a healthier planet.
V2G and Smart Grid Integration
The role of smart grids in enabling V2G
Smart grids, with their advanced metering, real-time monitoring, and analytical capabilities, are indispensable for V2G. They provide the necessary infrastructure for the dynamic, two-way communication between EVs and the grid, enabling the granular control and optimization required for effective V2G deployment.
Enhancing energy efficiency and distribution
By integrating V2G with smart grids, we can unlock even greater efficiencies in how we produce, distribute, and consume electricity. This combination has the potential to revolutionize the energy landscape, enabling more personalized energy solutions and facilitating a more sustainable and resilient grid.
Examples of successful V2G and smart grid integration
There are already promising examples of V2G and smart grid integration around the world, from pilot projects in Denmark and the Netherlands to larger-scale implementations in California and Japan. These initiatives demonstrate the feasibility and benefits of V2G, providing valuable lessons and blueprints for future endeavors.

Case Studies: V2G in Practice
Pilot projects and their outcomes
Numerous pilot projects have showcased the diverse applications and benefits of V2G technology. From fleet operations in university campuses to residential trials, these projects have demonstrated V2G’s viability in reducing energy costs, supporting grid services, and increasing renewable energy usage.
Countries leading in V2G technology
Denmark, the Netherlands, Japan, and some states in the US, like California, are at the forefront of V2G adoption. These regions have the regulatory frameworks, technological infrastructure, and market incentives that foster innovation and investment in V2G technology.
Lessons learned from current implementations
The key takeaway from existing V2G implementations is the importance of stakeholder collaboration – between government bodies, technology providers, grid operators, and end-users. Additionally, ensuring user engagement and clear communication around the benefits of V2G are crucial for its widespread acceptance and success.
Policy and Regulatory Framework for V2G
Existing policies supporting V2G
A growing number of regions are developing policies to support the integration of V2G technology. These range from financial incentives for buying V2G-capable EVs to investments in charging infrastructure and pilot programs to test different V2G business models.
The need for standardized regulations
For V2G to reach its full potential, standardized regulations across markets are essential. This includes technical standards for charging equipment, protocols for data exchange, and guidelines for compensating EV owners who participate in V2G programs.
Stakeholder roles in shaping policy
Building a supportive ecosystem for V2G involves all stakeholders – from policymakers and utilities to EV manufacturers and consumers. By working together, these groups can address the current barriers to V2G adoption and shape a future where electric vehicles play a central role in our energy system.